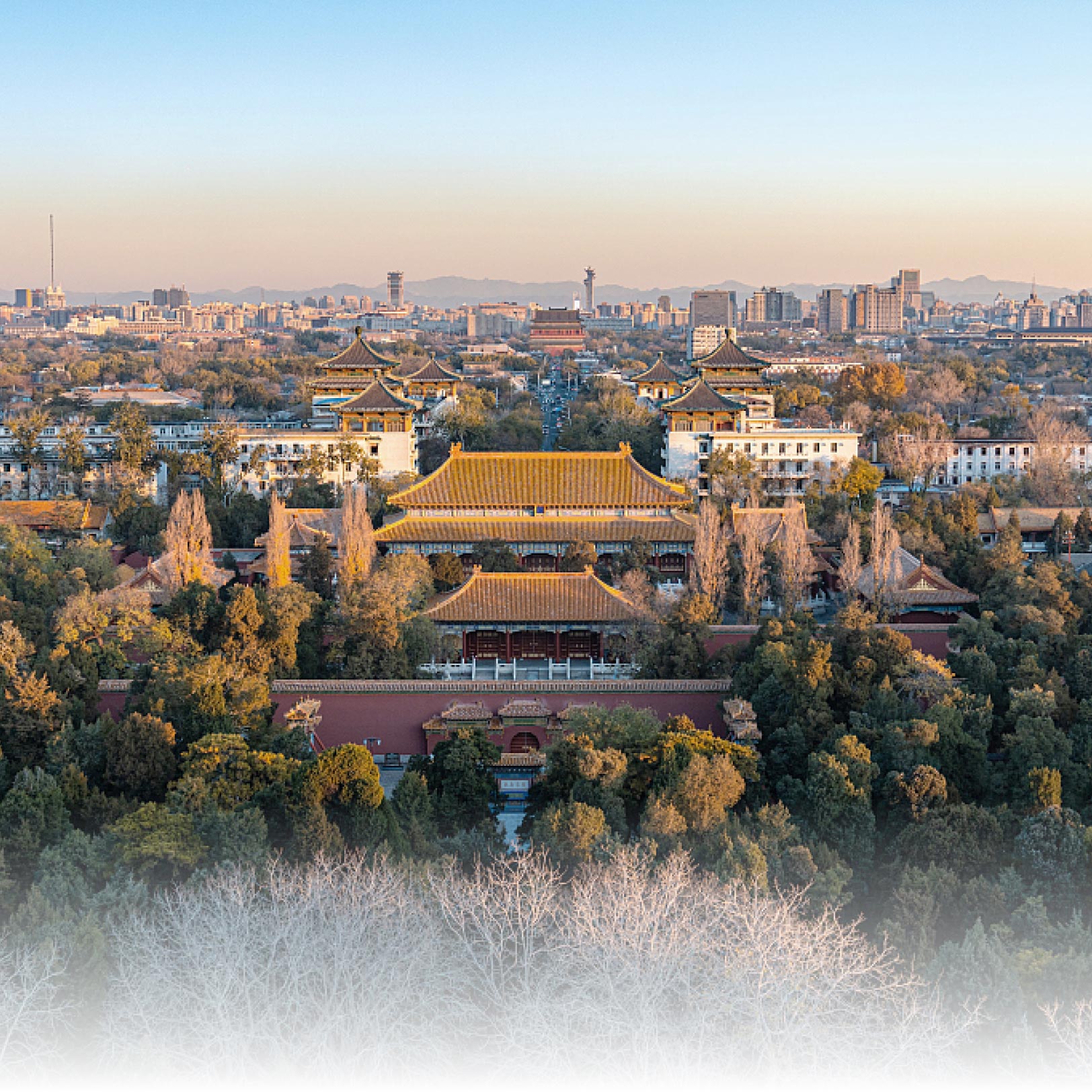
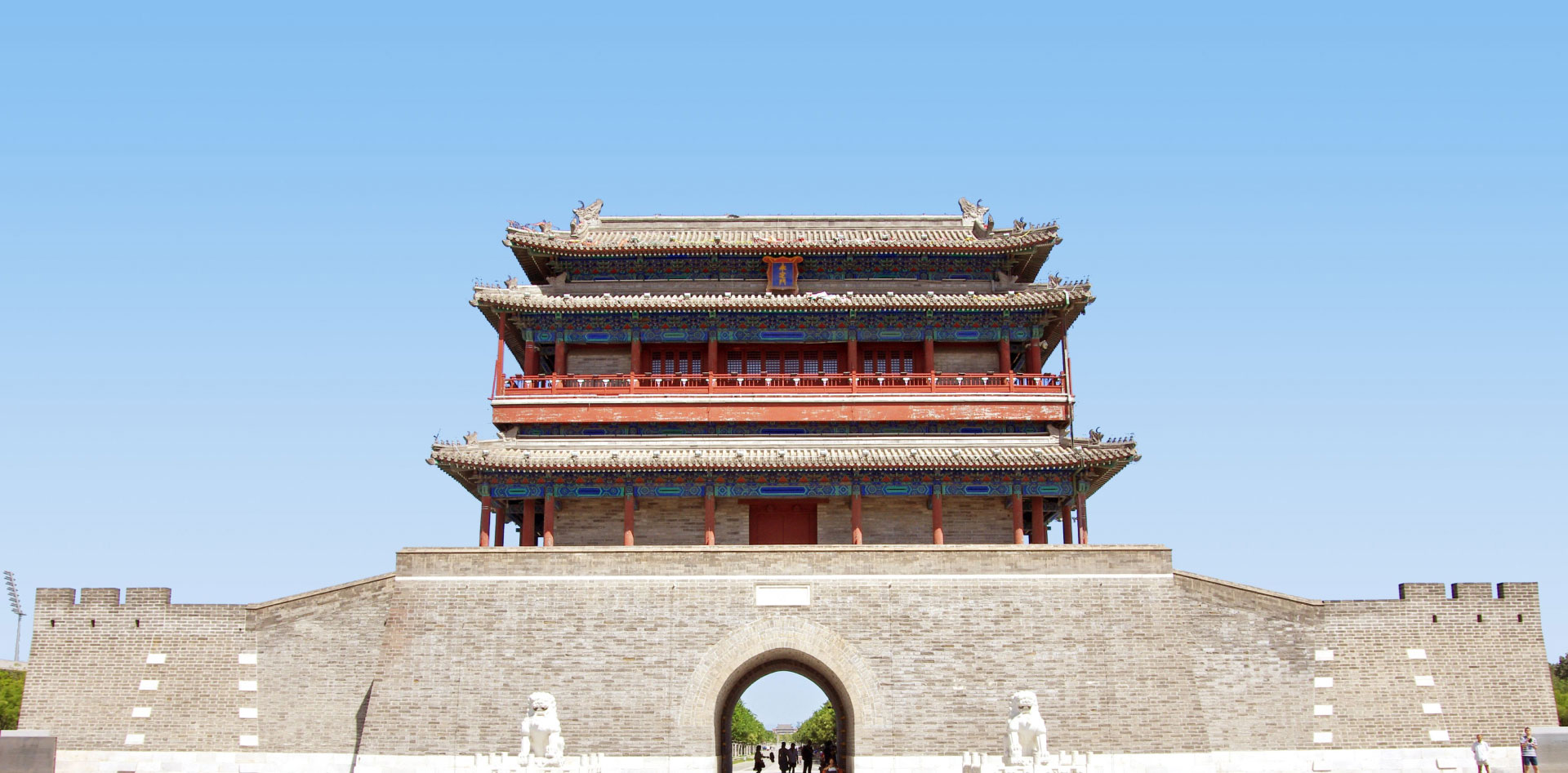
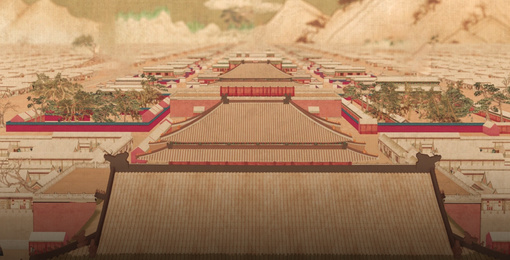
The Yongdingmen Gate, the southern portal of the outer city of the old city of Beijing, is the historical landmark of the southern end of Beijing Central Axis. It comprises the reconstructed city gate tower and the pavements on the ground showing the historic placement of the wengcheng barbican on the south side, providing an essential scenic spot for viewing the landscape of the south section of the axis.
The Yongdingmen Gate was the southern portal of the outer city of Beijing during the Ming and Qing dynasties. It is the highest ranked of the seven gates in Beijing's outer city, exhibiting the superior status of the buildings on Beijing Central Axis and providing a unique testimony to the methods of traditional urban management during the Ming and Qing dynasties. The existing Yongdingmen Gate is a historical landmark for marking the site of the original Gate which was demolished in 1950s and rebuilt in 2005 strictly following the Principles for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage Sites in China. The location of the gate tower marks the position of Beijing Central Axis' southern end, exhibiting the traditional forms and architectural techniques applied in constructing city gate towers in ancient China. It is an essential scenic spot for viewing the landscape of the south section of Beijing Central Axis.
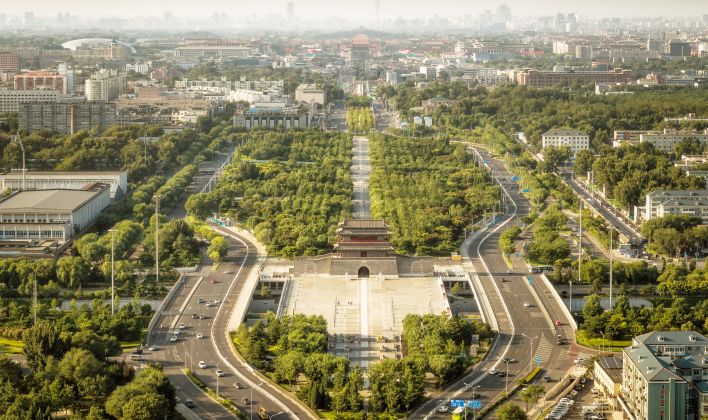







The Yongdingmen Gate Tower was rebuilt in line with its original form for the purpose of presenting its historical location. The former wengcheng barbican's site on the open ground, south of the gate tower, is also marked out, accurately showing the historical relationship between the gate tower and the wengcheng barbican.

As the south gate of Beijing's outer city, the Yongdingmen Gate was an important part of the urban defense system and management facilities in the Ming and Qing dynasties. It was also part of the national etiquette system. With the rise of business and trade in the outer city of Beijing, the population inside the Yongdingmen Gate grew increasingly while handicrafts and commerce thrived. The Yongdingmen Gate thus became an essential passage for merchants and traders. The reconstructed Yongdingmen Gate Tower and the paved marking of the barbican on the ground unmistakably identify the position of Beijing Central Axis' southern end and accurately display the Yongdingmen Gate's historical design and traditional craftsmanship.
The Yongdingmen Gate was first built in 1553. In order to build up Beijing's defense during the Ming dynasty, seven city gates were built for the outer city, with the Yongdingmen Gate being the largest and the highest ranked. The wengcheng barbican was added on the south side of the Yongdingmen Gate Tower in 1564. The archery tower was built on the wengcheng barbican in 1750. In the 1950s, Beijing was developing rapidly and the problem of traffic congestion in the Yongdingmen area became increasingly acute. In 1951, the Yongdingmen Gate's wengcheng barbican was demolished to open up traffic inside and outside the old city of Beijing. The Yongdingmen Gate Tower and Archery Tower were demolished in 1957 to relieve traffic pressure. The southern moat was dredged and straightened, and the roads and streets in the Yongdingmen area were widened simultaneously. The Beijing Municipal Institute for Cultural Heritage carried out archeological excavation work on the site of the Yongdingmen Gate in 2003. Seven exploratory trenches of different lengths were excavated to determine the gate tower's boundary. The Yongdingmen Gate's reconstruction project started in 2004 and was completed in the following year. The reconstruction work was strictly based on the archeological findings and research results from the historical records. The reconstructed Yongdingmen Gate identifies the southern end of Beijing Central Axis.